If a couple has been trying to conceive for more than a year and no pregnancy has been achieved, then there are obvious concerns. Therefore, that is the time when these couples start making doctor’s appointments to discuss how they have not been successful with conceiving a child. Pregnancy pills may be prescribed or fertility treatments offered. Claim Your 20 Free Pregnancy Tests – Click Here
The first thing the physician will do is have the man have his sperm count and quality tested. If everything checks out and there are no concerns, then the woman will be examined.
The physician will likely be referring the couple to a fertility specialist at this point. Before the woman starts taking any drugs, her ovaries, uterus and fallopian tubes will be checked.
Blood work will be done as well, however, blood work may not indicate that anything is off so therefore, it is not always reliable when it comes to indicating that a fertility issue is at play.
The uterus and ovaries will be checked via ultrasound, and the fallopian tubes will be checked through a procedure called a hysterosalpingogram (HSG). A HSG involves the use of an X-ray to look at your fallopian tubes and uterus. Most of the time it can take about 5 minutes to do, and the patient can go home the same day.
If everything checks out and the tubes are open, then the next step is taken and that is the start of taking fertility drugs.

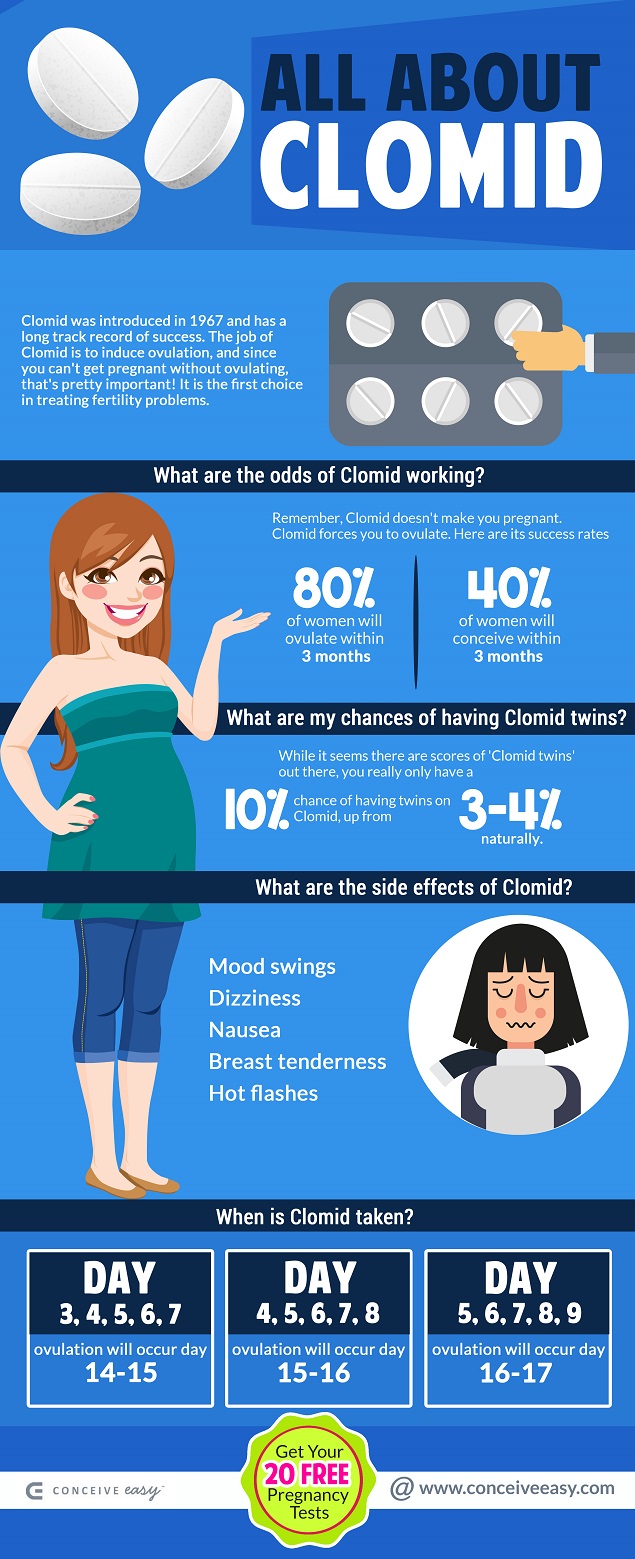
There are many fertility drugs that help conception happen, however the first drug that fertility specialists always use is clomiphene citrate. Clomiphene citrate is also referred to Serophene or Clomid. Clomid is the most common name for the drug, and hence this is the name that will be used in this article.
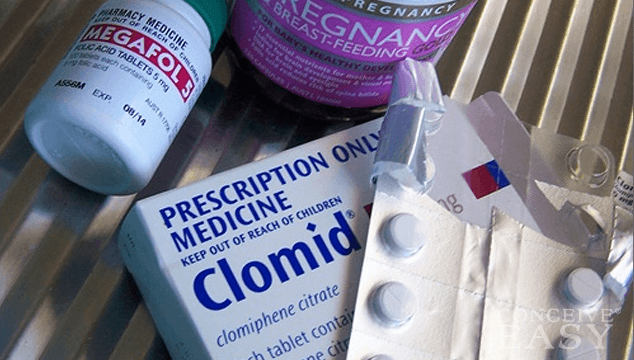
What is the job of Clomid? To induce ovulation!
That is it, because if there is no ovulation, then a pregnancy will not happen! And just because a woman gets periods does not always mean she is ovulating. In those cases the periods will be irregular most of the time. And blood work will not necessarily show the reason behind anovulation.
The reason that Clomid is the first choice of treating fertility problems among specialists is because it relatively safe and is the weakest medication among others.
In fact, Clomid is one of the first fertility drugs that was ever to hit the market as it was introduced in 1967.
Clomid at the time was used as infertility injections, however now Clomid comes in a tablet form. However, as stated previously, Clomid is the weakest fertility drug around, and therefore it is not necessarily suitable for all women and all causes of infertility. Many women will need a more powerful drug.
The only times that Clomid will not be first prescribed is if other issues that may not be getting in the way of ovulation such as blocked fallopian tubes, or structural issues with the uterus being the obvious causes of infertility. Steps such as in vitro (IVF) or perhaps even surrogacy will be looked into in those cases right away.

However, again if nothing is noticeably wrong, then Clomid will immediately be prescribed.
Clomid is most effective when used by women who have polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) which is caused by high levels of testosterone in a woman’s body which can impede regular ovulation.
Again, it’s all about ovulation!
Clomid can also be helpful for women who have luteal phase deficiency (LPD) which is the period between ovulation and menstruation being too short. Most of the time a healthy luteal phase is from 12-14 days after ovulation allowing a fertilized embryo to implant in the uterus.
If it is too short, there isn’t enough time for a fertilized egg to implant… hence no pregnancy!
In this case, Clomid can help with correcting LPD. The cause of LPD is when the ovaries don’t produce enough luteal hormone (LH). LH stimulates the thickening of the blood supply in the uterus which helps to maintain this supply during pregnancy. If the level of LH drops, the uterine lining will shed. That said, if the luteal phase is under 11 days after ovulation, then a fertilized embryo will not implant in the uterus and be lost during the time Aunt Flo pays a visit.
Sometimes Clomid can help with unexplained infertility that have nothing to do with anything structurally wrong either.
Clomid reduces the production of estrogen which sounds counterintuitive since women need estrogen to have their reproductive systems working properly.
Here is something that the average individual would not know.
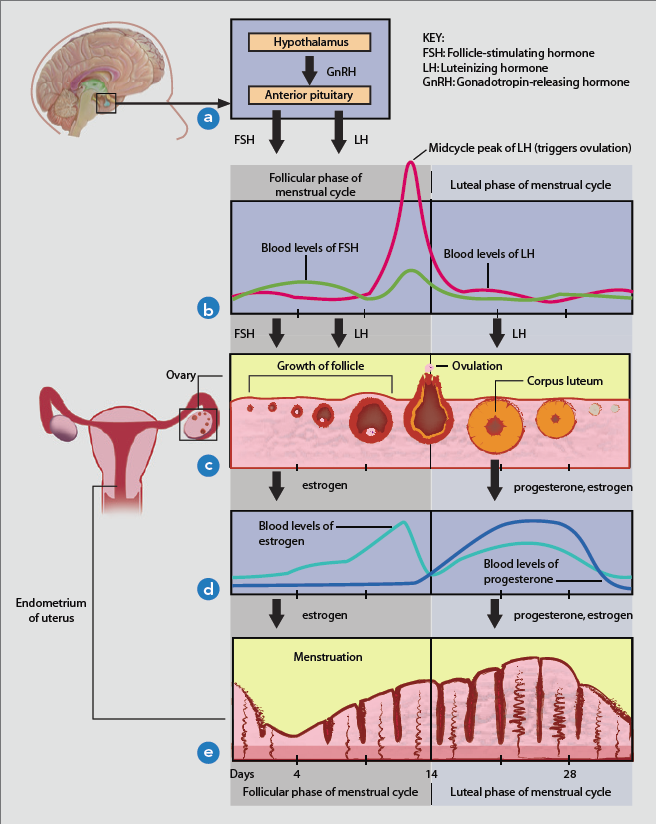
Low estrogen levels can trick the pituitary gland and cause it to produce more follicle stimulating hormone which is also referred to FSH, as well as LH hormones.
FSH and LH stimulate follicle and egg production in the ovaries, therefore egg production can be strengthened. In fact at times more than one egg can be matured and released per cycle when Clomid is taken. This really is a great drug for women who produce eggs sporadically. Therefore, by forcing ovulation each month, it will increase the likelihood of conception happening.

Most of the time, women don’t have side effects that are too distressing. It is common for Clomid to cause mood disorders, dizziness, nausea, breast tenderness and hot flashes. Even though these side effects are unpleasant, they are manageable.
Ever heard Clomid called Clo-moody?
It is rare for Clomid to cause ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) like other fertility drugs can, which is as it sounds – hyper or overstimulation of eggs. That is because it is rare for Clomid to release more than three mature eggs in one cycle. OHSS causes the ovaries to become swollen and painful, and that is not something that happens with Clomid except maybe in the rarest instance. However, taking Clomid for one than a year, there is a slight increase in risk for ovarian cancer.

Clomid is taken for five days. Either on day 2, day 3, or day 5 of your cycle, you begin taking Clomid, for 5 straight days. If you take Clomid on day 2, you take it until day 6. If you start on day 5, then you stop on day 9. Then ovulation is supposed to happen about 5-9 days after you take your last dosage.

Clomid works the best when the lowest dose that successfully causes ovulation is used. The vast majority are prescribed 50mg, and for most women, this will do the trick. Therefore, if a woman ovulates on 50mg of Clomid, which is the lowest, then the next dosage up which is 100mg will not likely cause her to ovulate more. She will just end up with more side effects.
However, if a woman doesn’t ovulate on 50mg of Clomid, then she will likely ovulate on 100mg. If not, then the next dose up will be tried which is 150mg to get an ovulatory response.
Some pregnancies will happen on Clomid dosages that are above 100mg. However, increasing the Clomid dose to 200mg does not result in more pregnancies. In this case, if Clomid fails to produce an ovulatory response on the highest dosage- then Clomid is not going to help at all.

Women who are prescribed Clomid in the first place, either don’t ovulate at all, or don’t ovulate on a regular basis. Therefore, they would have no idea what signs to look for when ovulation is on its way or happening. There are several methods that can be used that will indicate when ovulation is about to happen:
• Calculation: Ovulation and Fertility Charting and Calculator
• Temperature Charting
• Cervical Mucus Changes
• Ovulation Predictor Kits
• Ultrasound Exams of Ovaries
Most fertility clinics will monitor patients who are taking Clomid by monitoring their cycles through ultrasounds. If a follicle is maturing and growing, then the ultrasound technician will record the growth and the size, and send it back to the fertility specialists. The fertility specialist will be able to tell you that ovulation is about to happen, and guide you when to have intercourse or artificial insemination.
The ultrasound will also show the measurement of the uterine lining. That is crucial for them to know because if a pregnancy does occur, a decent amount of lining will indicate that a successful implantation will be likely.

These blood tests are taken in conjunction to cycle monitoring via ultrasound. However, progesterone hormones will be tested via daily blood work until the LH surge happens which indicates that ovulation is imminent.
However, some fertility clinics may give you the option to monitor ovulation on your own if you want to save money. There are ways to do that.

This particular method is not the most useful method while you are on Clomid, because by the time there is a rise in temperature, ovulation has already happened and if you have intercourse after, fertility won’t likely happen because an egg released is only good for 24 hours- then it begins to die off.
The rise in BBT only happens when ovulation has already occurred which would translate into a wasted month unless intercourse happens right after the temperature increase.
However, if you keep in mind that ovulation could happen 5 days after taking Clomid, you can start having intercourse within that time period. If you had intercourse a day before the rise was noted in your BBT, then there is a good chance that pregnancy could happen due to the fact that sperm is inside of your tract.

Your cervical mucous goes through changes in its consistency through the cycle. After the period is over, it is thin but as time goes on nearing ovulation, it becomes thick and stretchy, and egg-like. If you notice the changes in the mucous while you keep in the mind that ovulation can happen as soon as 5 days after taking Clomid, then it is the time to get busy!
Ever heard of egg-white cervical mucus? That’s the fertile kind!

When a woman is ovulating, sometimes dull abdominal pains can be felt, and this kind of ovulation discomfort is called Mittelschmerz. This method alone is not always reliable either because there are different factors that can cause you to have abdominal discomfort.

However, again if you begin to have intercourse within 5 days of taking Clomid and you feel these pains, then there is a good chance that you have ovulated or are about to ovulate. If sperm is inside from having intercourse before, then the chance of achieving a pregnancy is high.

OPK’s are way more reliable than taking your BBT, because they measure your LH which indicates that ovulation is on the way if a rise begins to happen – on that very day! This way you will see right then and there that ovulation is ready to happen and take advantage of that time to have intercourse to increase the odds of achieving a pregnancy.
A positive OPK means it’s time to get busy!

You have to remember. Clomid doesn’t get your pregnant. Clomid forces you to ovulate. And since Clomid is an effective treatment to trigger ovulation, it therefore helps a pregnancy happen. Here are the odds of its effectiveness:
80% of women taking Clomid will successfully ovulate within the first three months
40% of women will conceive within the first three months
The live birth rate for women taking Clomid falls somewhere between 30% and 60%
Clomid increases the chance of having twins by 10%

If pregnancy is not achieved within six months, most fertility clinics will discontinue the use of Clomid and try other drugs.
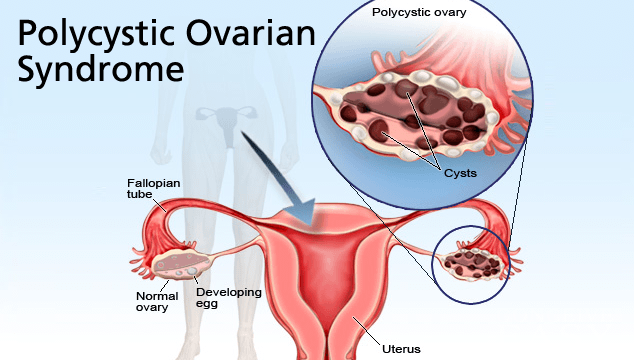
Some women with PCOS may need to take Metformin in conjunction with Clomid if insulin resistance is getting into the way of a proper ovulation from happening. In many cases Metformin and Clomid are successful if taken together.
However, in some cases there could be other hormonal factors as to why women are not ovulating which Clomid won’t be able to treat. Therefore, these women will have to go on more aggressive fertility treatments such as:
Femara or letrozole and other aromatase inhibitors, which is similar to Clomid but is more intense.
Injectable gonadotropins such as the GnRH pump and injectable FSH hormone products which triggers FSH production for ovulation.
Bromocriptine which reduce prolactin levels if high prolactin levels are the cause of anovulation.
In other words, if Clomid doesn’t end up working, there is hope that another fertility treatment will help you achieve that pregnancy. However, in most cases Clomid will do the trick and if you are on Clomid to help stimulate ovulation, best of luck in achieving that dream pregnancy!









Comments